Follow us on Telegram for the latest updates: https://t.me/mothershipsg
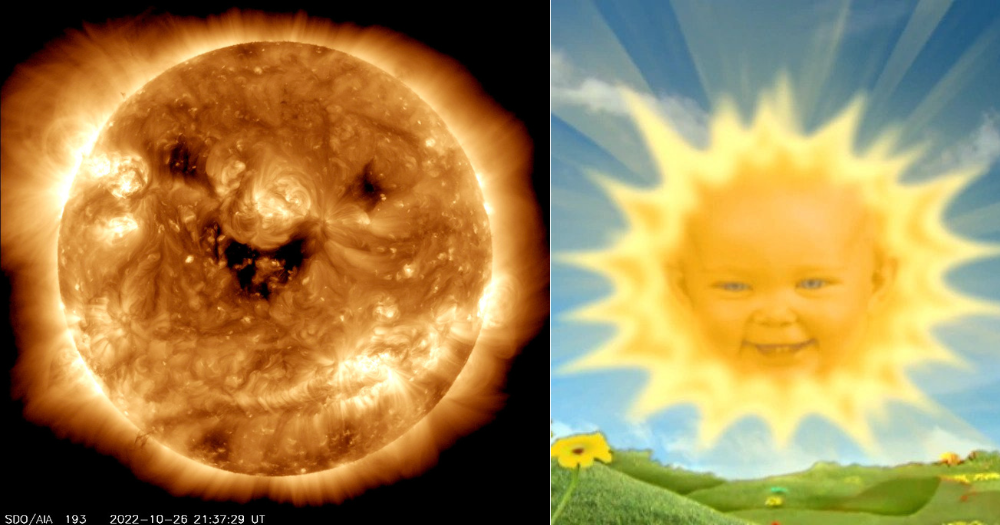
Researchers at the NASA Solar Dynamics Observatory captured a unique sight of the Sun on Wednesday (Oct. 26).
In a tweet on Oct. 27, the U.S. space agency posted a photo of the sun "smiling".

The anthropomorphic look that gave the Sun a, erm, sunshiny disposition, is the result of "coronal holes", NASA wrote in the tweet.
These holes are the result of "fast solar wind gushes out into space".
Looks familiar
If you grew up watching "Teletubbies", you might be glad to know that the producers of the show were right all along, as Twitter user @ethanisaac01 pointed out:
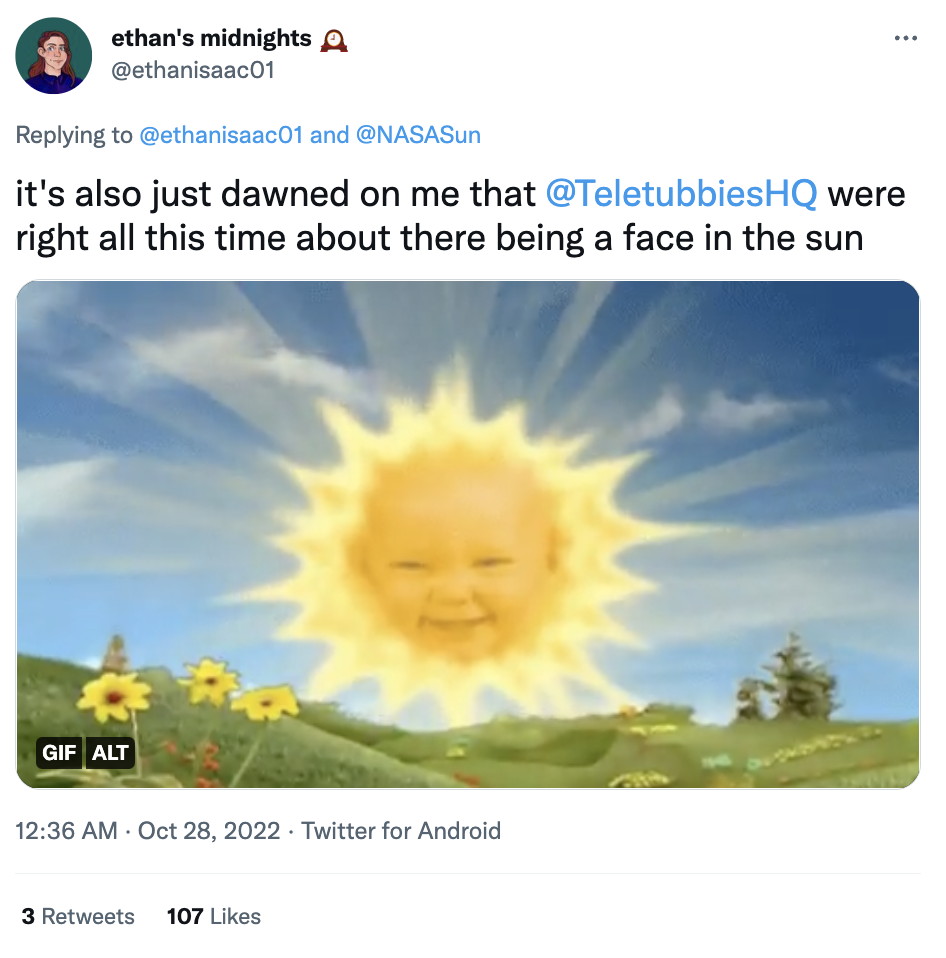
Another user found the smile a little more sinister, seeing in it a resemblance with the Stay Puft marshmallow man from "Ghostbusters":

This meme by @Emma_Quirk tops it all off:
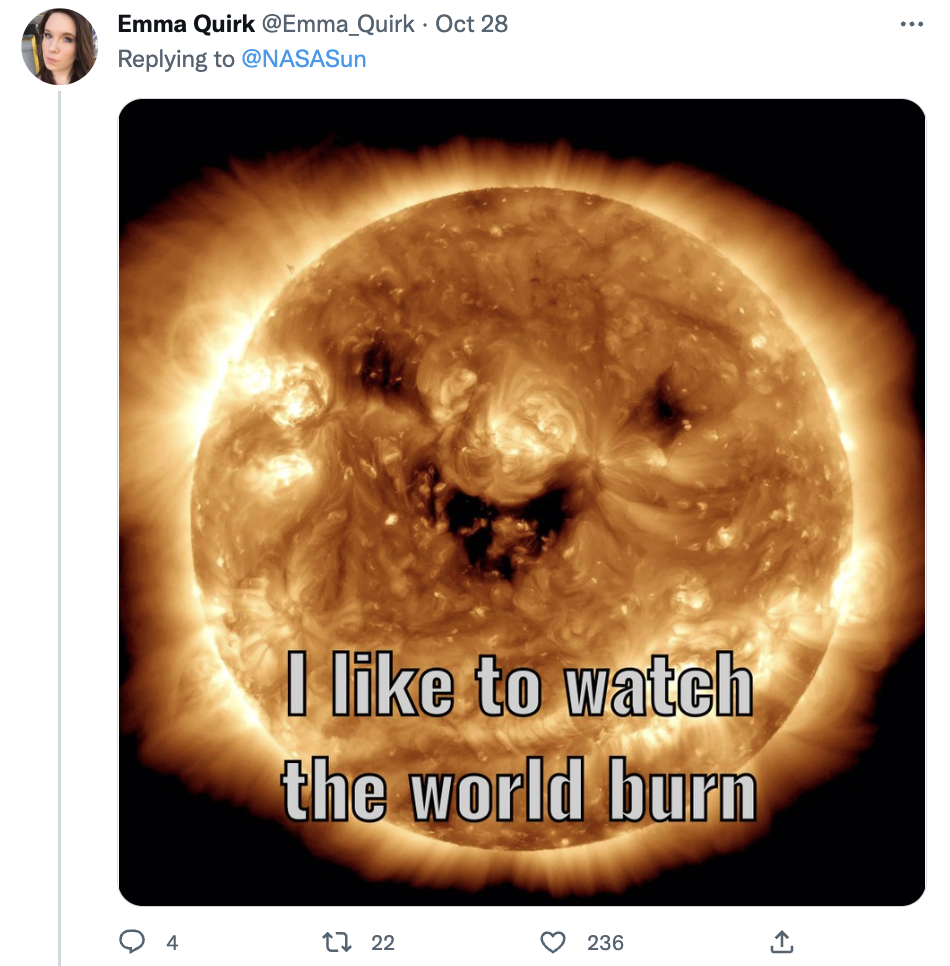
Seeing the Sun in a different light
The NASA department behind Wednesday's image, the Solar Dynamics Observatory, studies the effects of the Sun on Earth and near-Earth objects.
Its semi-autonomous spacecraft is pointed at the Sun almost continuously, observing the Sun through various filters along the light spectrum and producing stunning images of the fireball in the sky.
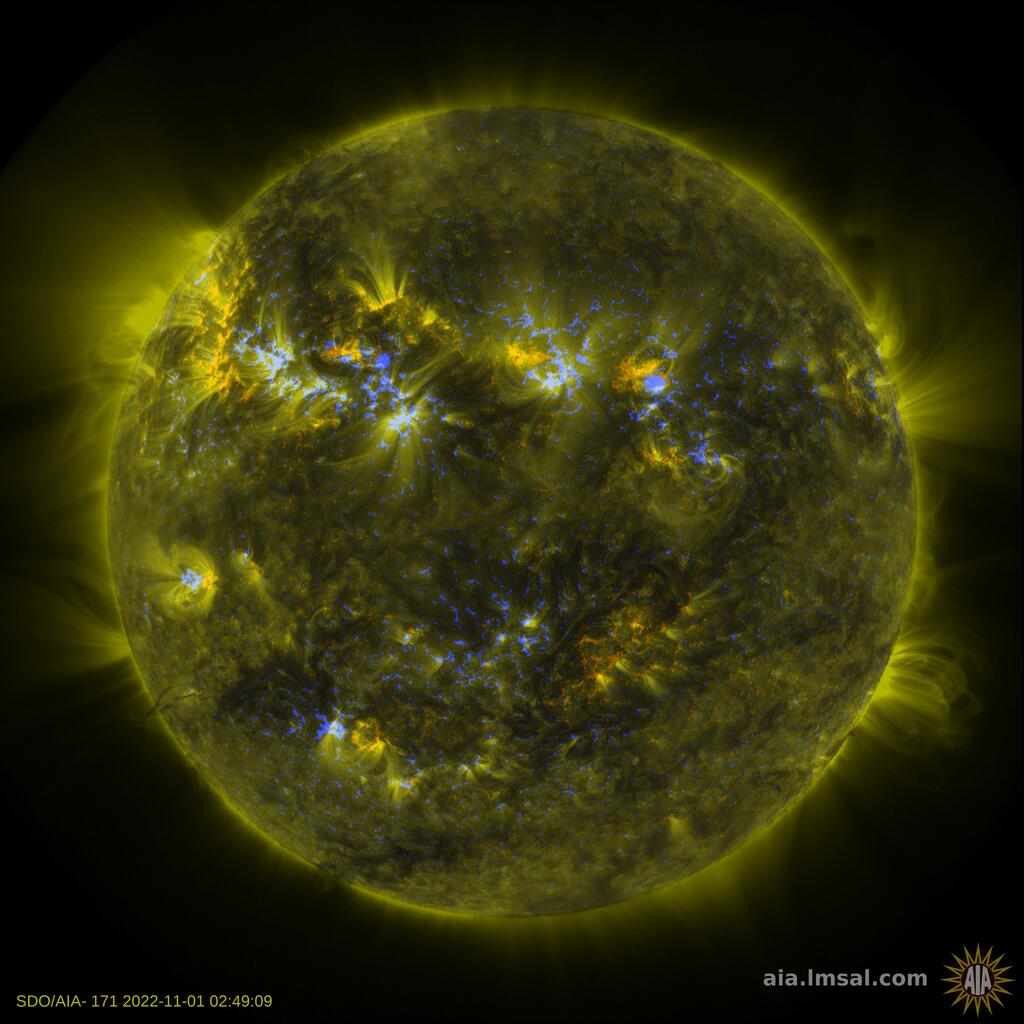 Image via NASA Solar Dynamics Observatory.
Image via NASA Solar Dynamics Observatory.
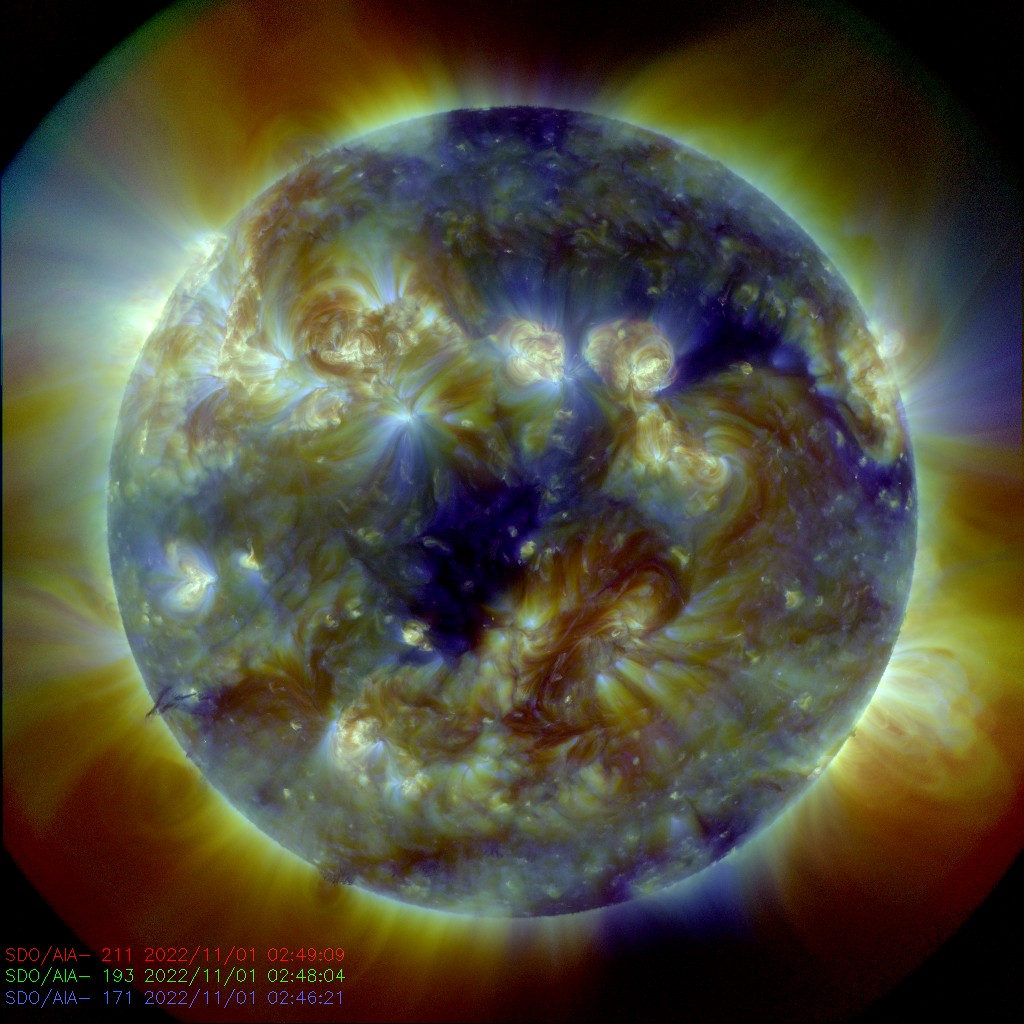 Image via NASA Solar Dynamics Observatory.
Image via NASA Solar Dynamics Observatory.
Wednesday's "smiling" Sun was observed via ultraviolet light, NASA said in the tweet.
What's solar wind?
The Sun's burning gases exists as plasma, a collection of charged particles.
Sometimes, the plasma gets so hot that the Sun's gravity cannot hold it down.
In these instances, the plasma is ejected out towards space from the Sun's outermost layer called the corona.
These plasma, travelling far distances, creates "solar wind".
The Sun's solar wind actually reaches the Earth quite often, and results in the phenomena famously known as the Northern and Southern Lights.
The lights are created when ejected particles from the Sun slip through the Earth's magnetic field and react with the Earth's atmosphere at the poles.
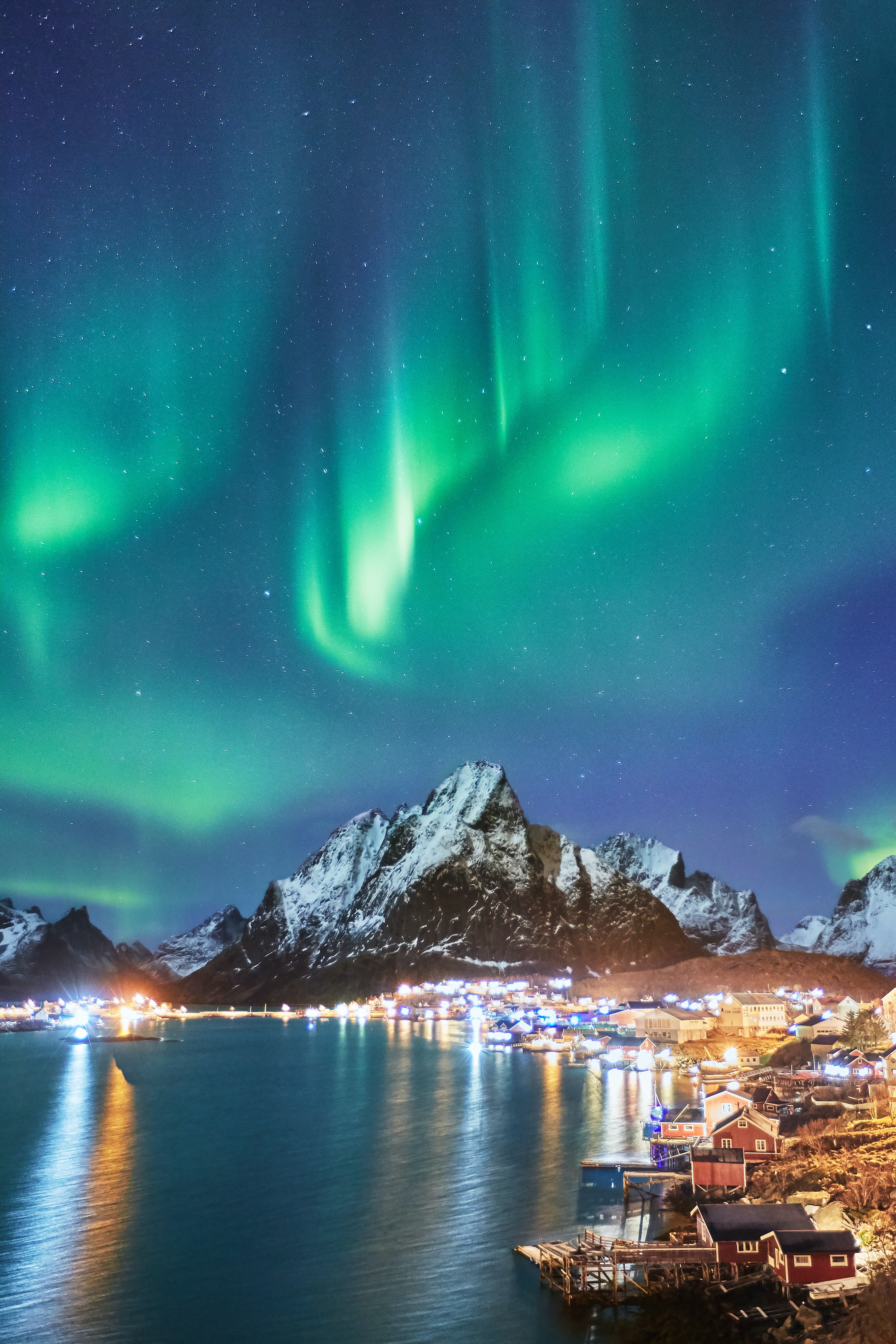 Image via Johnny Goerend/Unsplash.
Image via Johnny Goerend/Unsplash.
Top image via NASA Solar Dynamics Observatory/Twitter, Teletubbies Wiki
If you like what you read, follow us on Facebook, Instagram, Twitter and Telegram to get the latest updates.
